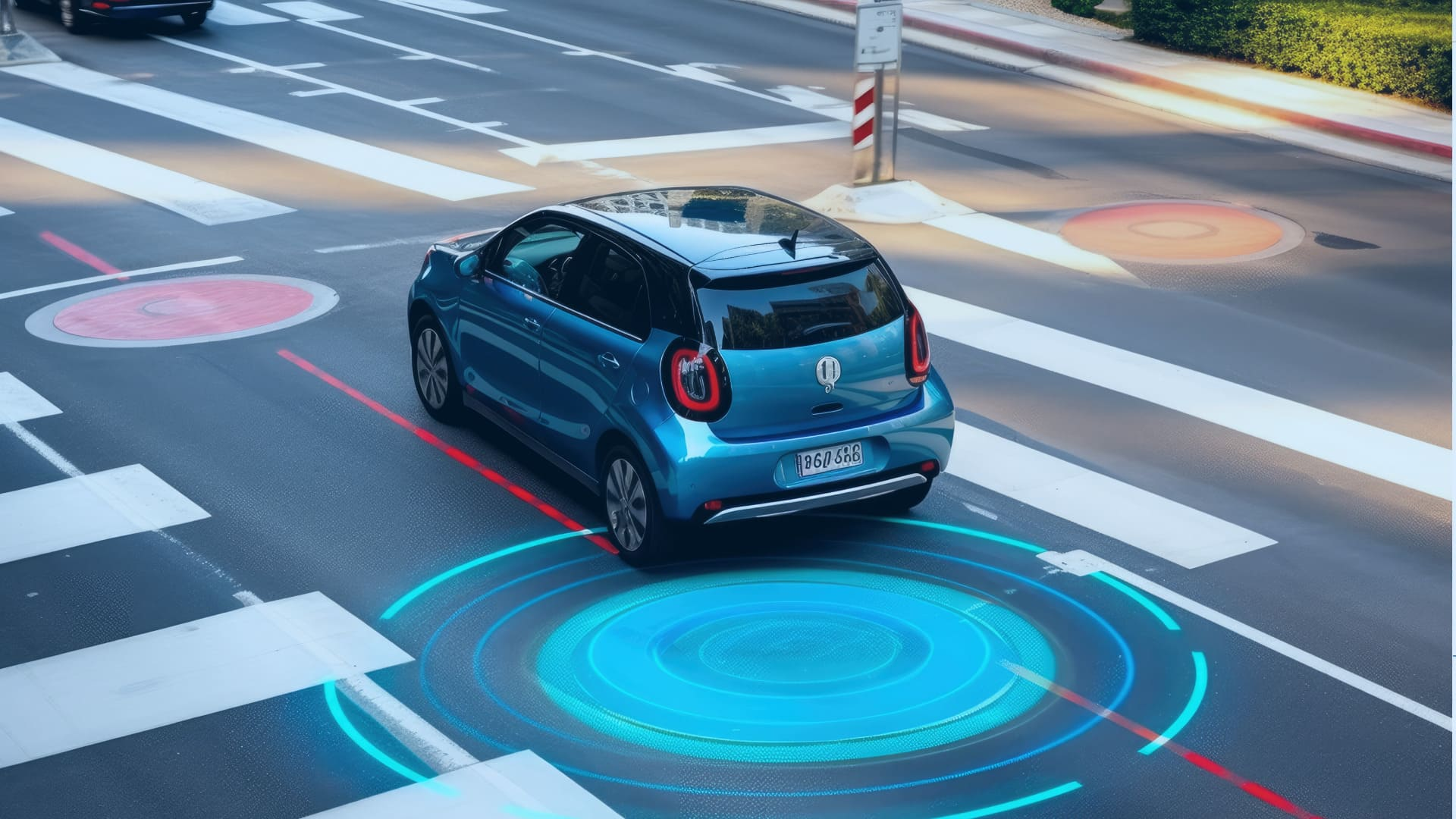
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) represent a significant leap forward in automotive technology, aiming to enhance road safety by assisting drivers in various aspects of vehicle operation. These systems utilize sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, detect potential hazards, and provide alerts or intervention when necessary. Here’s an in-depth look at how ADAS technologies are contributing to safer roads:

1. Collision Avoidance Systems:
ADAS includes collision avoidance systems such as forward collision warning (FCW) and automatic emergency braking (AEB). FCW uses sensors to detect objects in the vehicle’s path and alerts the driver to potential collisions. AEB takes it a step further by automatically applying brakes if the driver fails to respond in time, reducing the severity of or preventing collisions altogether.
2. Lane Departure Warning and Lane-Keeping Assistance:
Lane departure warning (LDW) systems use cameras to monitor lane markings and alert drivers if they unintentionally drift out of their lane. Lane-keeping assistance (LKA) systems go beyond warnings by actively steering the vehicle back into its lane if corrective action is not taken, enhancing vehicle stability and reducing the risk of side-swipe collisions.
3. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC):
ACC uses radar or cameras to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead by automatically adjusting the vehicle’s speed. It enhances convenience on long drives while reducing the likelihood of rear-end collisions caused by sudden braking or changes in traffic flow.
4. Blind-Spot Monitoring (BSM):
BSM systems use sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots and provide visual or audible alerts when it’s unsafe to change lanes. This technology improves driver awareness and reduces the risk of collisions during lane changes.
5. Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA):

RCTA systems warn drivers of approaching vehicles or pedestrians when reversing out of parking spaces or driveways, helping to prevent accidents in busy parking lots or residential areas with limited visibility.
6. Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR):
TSR systems use cameras to detect and recognize traffic signs, including speed limits, stop signs, and other road regulations. They display relevant information on the vehicle’s dashboard or head-up display, helping drivers stay informed and comply with traffic laws.
7. Pedestrian Detection and Collision Mitigation:
Pedestrian detection systems use cameras and sensors to identify pedestrians or cyclists in the vehicle’s path. They provide alerts to the driver and, in some cases, automatically apply brakes to avoid or mitigate collisions, especially in urban or congested areas.
8. Enhanced Visibility and Night Vision:
Some ADAS incorporate night vision cameras or infrared sensors to improve visibility in low-light conditions. These systems detect pedestrians, animals, or obstacles beyond the range of headlights, alerting drivers to potential hazards and enhancing safety during nighttime driving.
9. Driver Monitoring Systems:
Driver monitoring systems use cameras and sensors to assess driver attentiveness and fatigue levels. They provide alerts if the driver shows signs of drowsiness or distraction, promoting safer driving behavior and reducing the risk of accidents due to driver fatigue.
10. Integration with Autonomous Driving:
ADAS technologies are paving the way for autonomous driving capabilities by laying the foundation for automated vehicle control and decision-making processes. While not fully autonomous, these systems gradually introduce features that enhance vehicle autonomy and safety.
Conclusion:
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) are revolutionizing road safety by leveraging cutting-edge technology to assist drivers, mitigate risks, and prevent accidents. As these technologies continue to evolve and become more widespread, they have the potential to significantly reduce traffic collisions, injuries, and fatalities. However, effective implementation and driver education are crucial to maximizing the benefits of ADAS and ensuring safe interactions between automated systems and human drivers on the road. With ongoing advancements and regulatory support, ADAS are poised to play a pivotal role in creating safer, more efficient transportation systems for the future.